Update: Our project was selected as an honorable mention for WPI's 2021 Robotics Engineering Provost Award!
Project Abstract
A variety of animals such as primates, dogs, and bears switch modes of locomotion between quadrupedalism and bipedalism to better complete certain tasks. However, very few robotic platforms can effectively combine the two forms of locomotion. A multi-modal robotic platform with such capabilities would provide additional adaptability in unstructured environments, broadening its potential applications. Therefore, we extended an existing quadrupedal platform with the capability to transition into a bipedal stance. In this project, we built a physical robot, developed an accompanying software stack with a reinforcement learning pipeline, implemented quadrupedal locomotion, and achieved stance transition in simulation. Our integrated hardware and software platform affords future roboticists the opportunity to test and develop more adaptable locomotion strategies and increase the functionality of robots more broadly.
Project Video
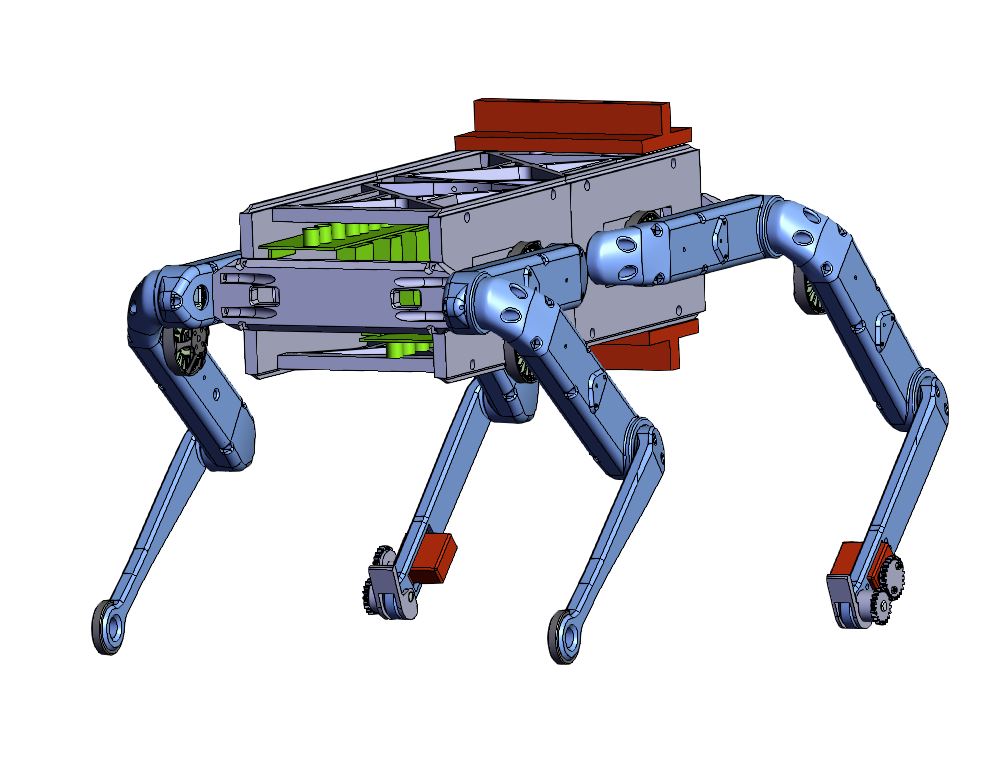
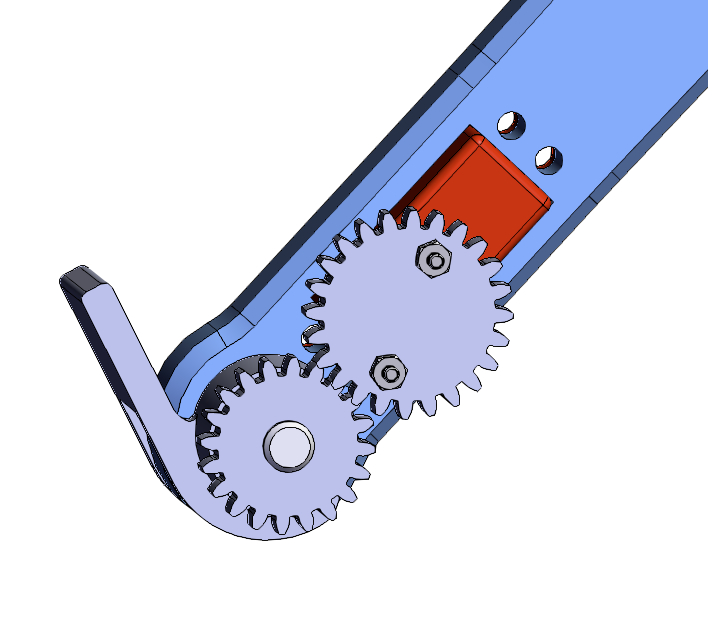
Solo 8 w/ a Foot
We are interested in creating a quadrupedal robot that is capable of standing bipedally. As such, we've had to modify existing designs to include a foot to increase our support polygon. Our design can be seen below.